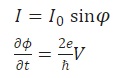| www.tmatlantic.com
Test & Soldering Equipment On-line Store |
|
D.E.V.I.C.E. (Wiki)Calculators Services |
|||||
Filter by first letter
|
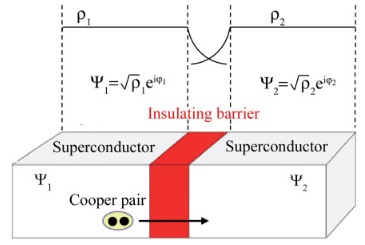
Josephson effectThe Josephson effects describe the transfer of Cooper pairs and the coupling of the macroscopic wave functions between two superconductors via a weak link. Some of the dependencies of such junctions are strongly related to the fundamental flux quantum. This gives excellent possibilities for application in measurement science and electronics. The Josephson effect was predicted in 1962 by Brian Josephson. He stated that a supercurrent could tunnel through an insulating barrier separating two superconductors. A Josephson junction is schematically represented by two superconductors separated by a thin insulation barrier. If the junction is biased with a dc current, the voltage across it remains zero up to a current value called Josephson critical current I0 due to the cooper pair-tunneling through the insulation barrier. This so-called dc Josephson effect occurs due to the overlap of the macroscopic wave functions in the barrier region.
When the bias current is greater than I0, the junction switches in a resistive state where the tunnel is due to the single electrons. The fundamental equations of the Josephson effect are as follows:
where I0 is the critical current and φ is the phase difference between the macroscopic wave functions of the cooper pairs relative to the two superconductors, and V is the voltage across the junction. |
|
Site mapPrivacy policyTerms of Use & Store PoliciesHow to BuyShippingPayment |