| www.tmatlantic.com
Test & Soldering Equipment On-line Store |
|
D.E.V.I.C.E. (Wiki)Calculators Services |
|||||
Filter by first letter
|
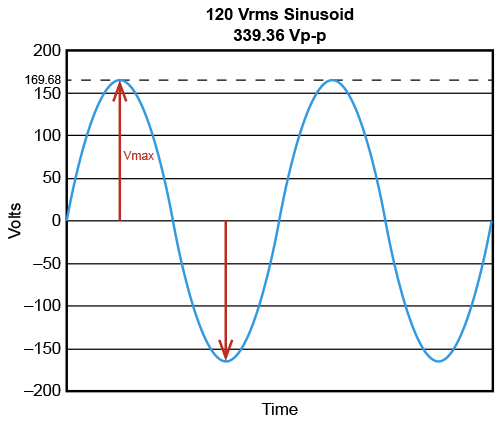
Relations between RMS voltage and peak-to-peak voltageThe illustration below shows that the wall socket voltage is actually 120 V and "formally" the peak-to-peak voltage is 339.36 V. You can see this value on your oscilloscope in the automatic measurements mode with Vpp mode ON.
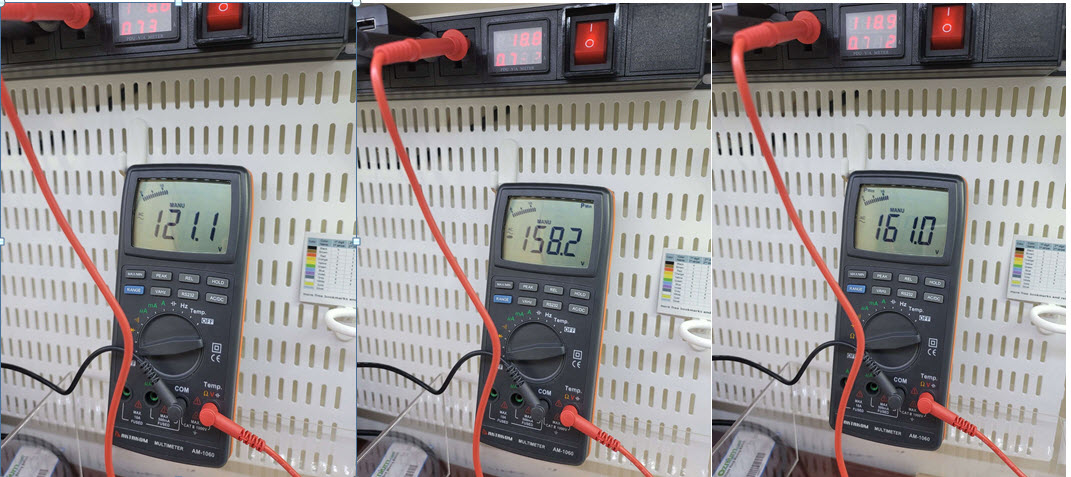
However in reality, there are no such values in a wall outlet. This is due to the fact that there is one Hot (Line) wire in the wall socket, and the second is Neutral, relative to which the Hot (Line) voltage changes. Thus, only Vmax can be on the Hot (Line) wire: +169.68 V or –169.68 V. Obviously, these values change with a frequency of 60 Hz. Some common multimeters, for example AKTAKOM AM-1060 DMM and those with Peak or Mix/Max mode can show close Vmax values. But keep in mind that these multimeters operate slower than 60 Hz and therefore the displayed values are approximate.
120V / 120V Peak(-) / 120V Peak(+) |
|
Site mapPrivacy policyTerms of Use & Store PoliciesHow to BuyShippingPayment |