| www.tmatlantic.com
Test & Soldering Equipment On-line Store |
|
D.E.V.I.C.E. (Wiki)Calculators Services |
|||||
Filter by first letter
|
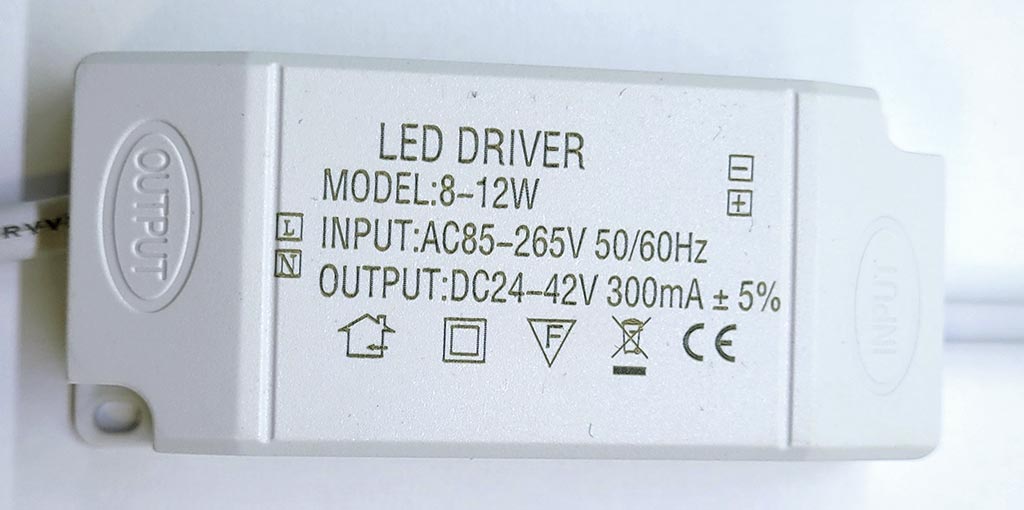
LED DriverLED Driver is a device used for powering LED lights. Depending on the type of LED connections in the light fixture, drivers are divided into:
1. Constant Voltage Drivers.
Drivers of this type are used both to power LED strips and white light fixtures, and to power LED strips and decorative lighting fixtures - called the RGB strip. Figure 2. Example of constant voltage LED Driver circuit 2. A constant current driver is a LED power device in a light fixture in which the voltage can vary over a wide range (see, for example, Fig. 3 - voltage range 24 - 42 v) but the current will be limited to a given value. Typically, current and voltage values are indicated on the driver housing.Drivers of this type are typically used to power LED strips and white light fixtures
DC Led Drivers can be made in various designs.
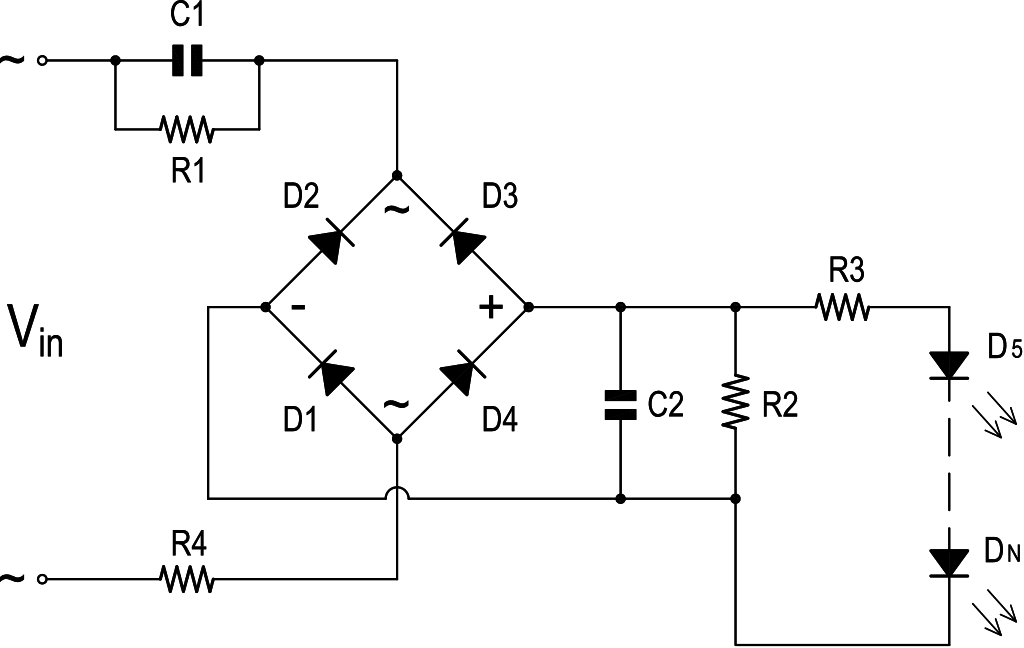
2.1. LED Driver based on the ballast capacitor. This is the cheapest option, but the most dangerous to use. An example of such a driver is presented in fig 4 and the most typical diagram in fig 5.
The disadvantage of this scheme is the direct connection of all circuits of the lamp, including the LED, to the high voltage of the electrical network. Figure 4. Example of a LED Driver with a ballast capacitor
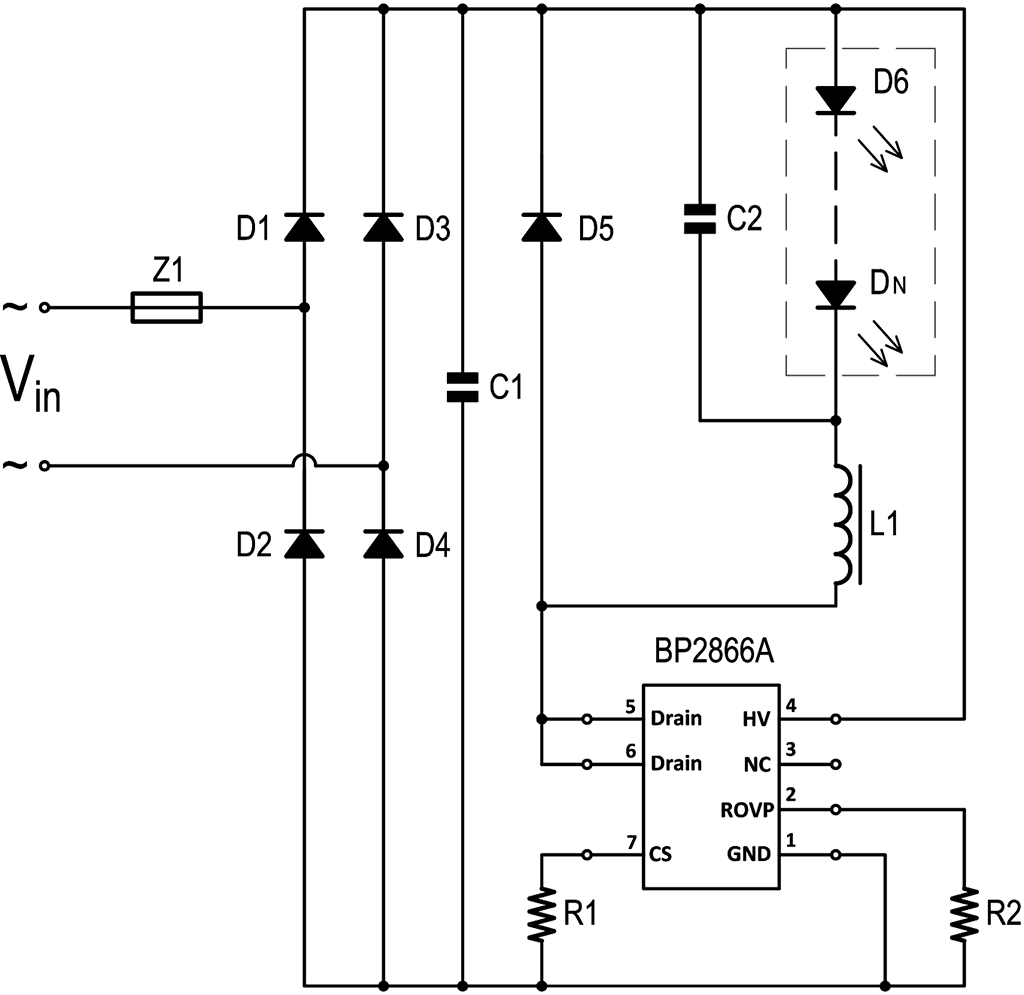
2.2. LED Driver Based on Inductor Figure 6. Example of an inductor-based LED driver
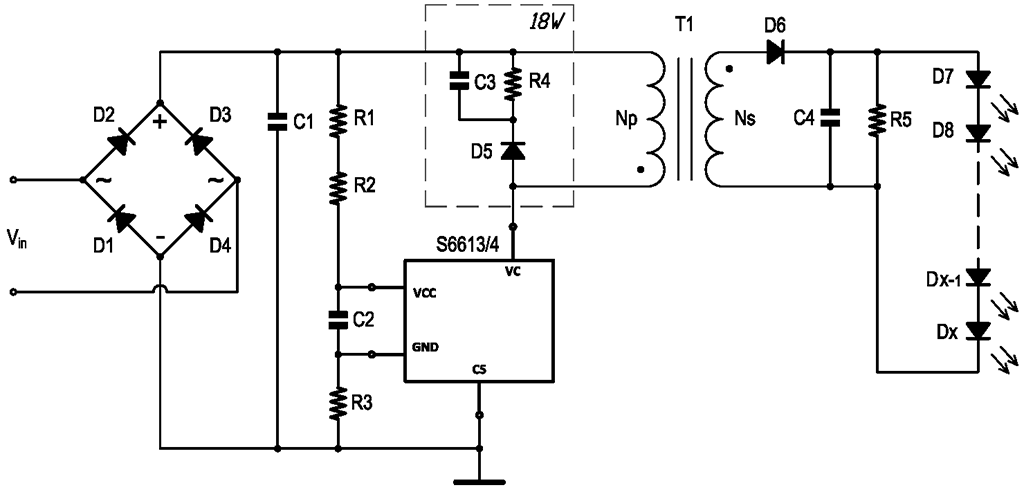
2.3. Led driver with decoupling transformer. This LED driver (see Fig 8) is based on a circuit for rectifying the input AC voltage to DC (D1-D4) and is based on an IC with a high-voltage MOSFET for generating pulse voltage (IC 6613S). This pulse voltage passes through the transformer (No), and the secondary winding (Ns) generates the voltage to power the LEDs in the light. The alternating voltage is rectified (D6, C4) and supplied to the LED light. The current control in the LED strip is controlled by resistor R3. The advantage of this type of driver is the galvanic separation of the high-voltage part and the low-voltage part for powering the LED.
LED Light Driver Repair and Redesign using AKTAKOM AM-1060 DMM |
Measurement History Events
Units Converter
|
|
Site mapPrivacy policyTerms of Use & Store PoliciesHow to BuyShippingPayment |