| www.tmatlantic.com
Test & Soldering Equipment On-line Store |
|
D.E.V.I.C.E. (Wiki)Calculators Services |
|||||
Filter by first letter
|
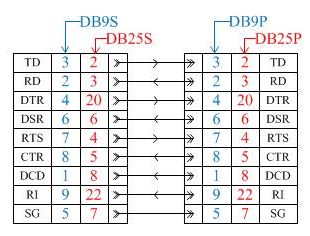
RS-232 (Recommended Standard 232)RS-232 standard is used to transfer data at a rate of several thousands of bits per second. Bipolar levels from ± 5 to ± 15V are defined by this standard. Besides that this standard describes interface control signals, data transfer and connectors types. There are asynchronous and synchronous modes of exchange provided by the standard but COM-ports support only asynchronous mode. An interface does not provide galvanic isolation of devices and requires a safety ground for connected devices if both of them are supplied by AC network and have network filters. This standard application allows using multi-core cables without any screening as the maximum voltage change rate of formers to minimize crosstalk is intentionally limited to 30 V/ms. In the standard modem connection cables with DB25P, DB9P plugs and DB25S, DB9S sockets are connected in accordance with the picture below:
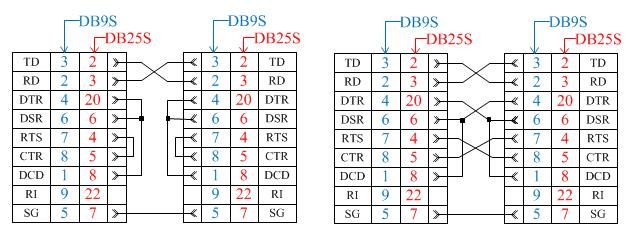
If devices are the same (2 computers) there are null-modem cables used because their sockets are the same:
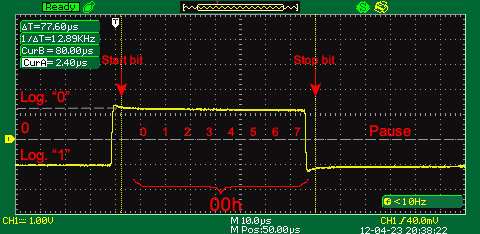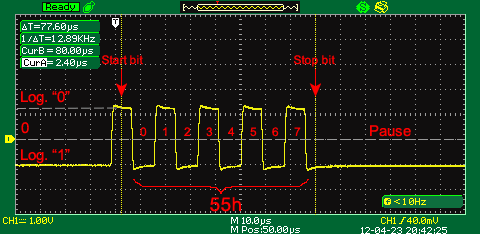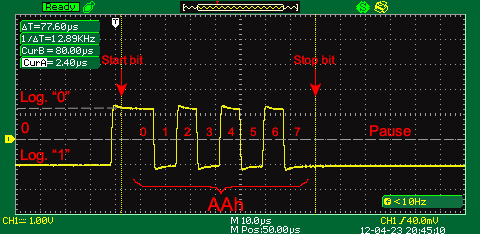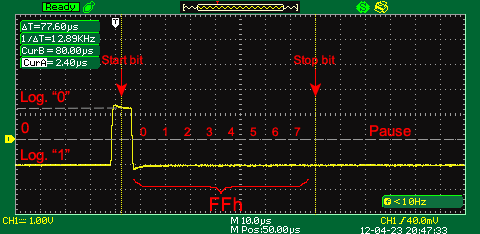
The animated picture below demonstrates a signal waveform in the data transfer loop sending 16 bytes of data with 00h, 11h, 22h,…FFh symbols without P parity bit
|
Measurement History Events
Units Converter
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Site mapPrivacy policyTerms of Use & Store PoliciesHow to BuyShippingPayment |