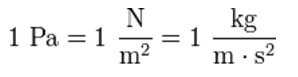| www.tmatlantic.com
Test & Soldering Equipment On-line Store |
|
D.E.V.I.C.E. (Wiki)Calculators Services |
|||||
Filter by first letter
|
Pascal (Pa)The pascal (symbol: Pa) is the SI derived unit of pressure, internal pressure, stress, Young's modulus and tensile strength, named after the French mathematician, physicist, inventor, writer, and philosopher Blaise Pascal. It is a measure of force per unit area, defined as one newton per square meter. Common multiple units of the pascal are the hectopascal (1 hPa = 100 Pa), kilopascal (1 kPa = 1000 Pa), megapascal (1 MPa = 1,000,000 Pa), and gigapascal (1 GPa = 1,000,000,000 Pa). On Earth, standard atmospheric pressure is 101,325 Pa. Meteorological barometric pressure reports typically report atmospheric pressure in hectopascals. The kilopascal is used in other applications such as inflation guidance markings on bicycle tires. One hectopascal corresponds to about 0.1% of atmospheric pressure slightly above sea level; one kilopascal is about 1% of atmospheric pressure. One hectopascal is equivalent to one millibar; one standard atmosphere is exactly equal to 101.325 kPa or 1013.25 hPa or 101,325 Pa. The corresponding Imperial unit is pounds per square inch (psi). The pascal can be expressed using SI derived units, or alternatively solely SI base units, as:
where N is the newton, m is the meter, kg is the kilogram and s is the second. |
|
Site mapPrivacy policyTerms of Use & Store PoliciesHow to BuyShippingPayment |