| www.tmatlantic.com
Test & Soldering Equipment On-line Store |
|
D.E.V.I.C.E. (Wiki)Calculators Services |
|||||
Filter by first letter
|
LAN (Local Area Network)
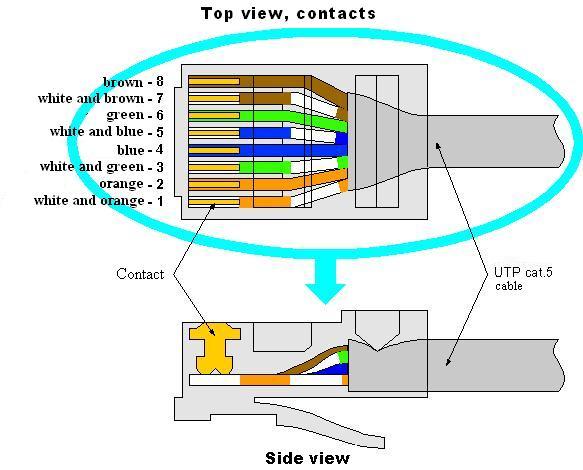
LAN is Local Area Network of a group of computers and/or any other devices placed at a relatively short distance and connected by specialized cables in order to exchange data and use common resources, such as printers, Internet access etc. Among the existing local network technologies the most popular is Ethernet technology with the use of twisted pair according to the standard topologies - star (common bus), ring or tree. At the same time several local networks can be united with other local networks, as well as with the Global Network, by means of gateways. For correct device addressing and data delivery only to a specified device in the network every device has unique identifiers: IP-address (Internet Protocol Address) and MAC-address (Media Access Control). In theory such addresses should be globally unique, that means they cannot be repeated both within the network and internetworking. But not all protocols use MAC-addresses and not all of those using MAC-address need such addresses to be so unique. To escape any conflicts connected with IP addresses, when there are two or more devices with identical IP addresses within one network, use DHCP protocol which allows computers to receive automatically IP-address and other parameters necessary to work in TCP/IP network. The order of cable cores (swaging) in RJ-45 for 100/1000 network for UTP Cat5E cable: 1 – white and orange, 2 - orange, 3 – white and green, 4 - blue, 5 – white and blue, 6 - green, 7 – white and brown, 8 - brown Meanwhile the swaging is the same for 100 Mbit/s and 1000 Mbit/s rates. For 1000 Mbit/s you need all 8 cores, for 100 Mbit/s – 4 cores is enough (1,2,3 and 6). There are two varieties of cable swaging – “straight” cable to connect PC to a switch (router), “reverse” – for PC-PC (PC-device) connection. Also there was “cross” cable used to connect two switches (obsolete term).
|
Units Converter
|
|
Site mapPrivacy policyTerms of Use & Store PoliciesHow to BuyShippingPayment |