| www.tmatlantic.com
Test & Soldering Equipment On-line Store |
|
D.E.V.I.C.E. (Wiki)Calculators Services |
|||||
Filter by first letter
|
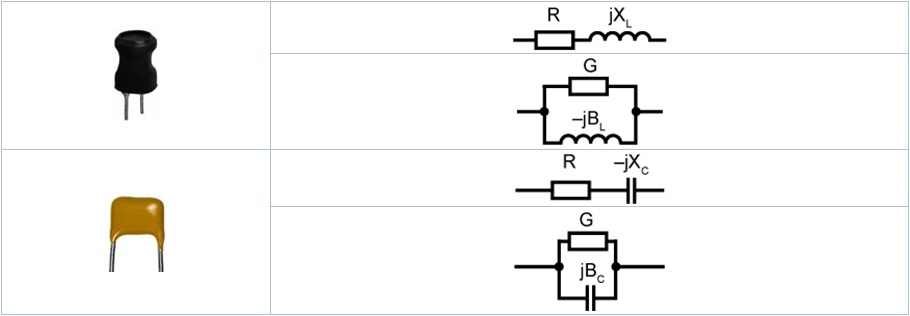
Series/parallel Equivalent ModeFor the presence of non-ideality and distributed parameters of components, actual components are usually equivalent to combined network of ideal components. In general, there are two simple equivalent models used in LCR meters, which are series model and parallel model:
Appropriate equivalent modes could help to gain better measurement results. Generally, Series mode is better for components with low impedance (below 100Ω), while parallel mode is for components with high impedance (over 10kΩ). For the components with the impedance between the two limits, equivalent mode has little effect on the testing result. In modern RLC measurers equivalent mode can be selected automatically. Besides series mode is selected for components with low impedance (below 10kΩ), it’s shown on a device display (e.g. Ls/Cs/Rs). For those components that have high impedance (over 10kΩ) there should be parallel mode selected and the display shows, for example, Lp/Cp/Rp. For the majority of devices equivalent mode can be selected manually.
|
Units Converter
|
|
Site mapPrivacy policyTerms of Use & Store PoliciesHow to BuyShippingPayment |