| www.tmatlantic.com
Test & Soldering Equipment On-line Store |
|
D.E.V.I.C.E. (Wiki)Calculators Services |
|||||
New Online Tool: Low Pass Filter Calculator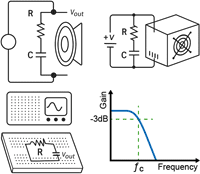
11/20/2025 Low pass filter calculator is an easy-to-use online tool to quickly determine the cutoff frequency of a low pass passive filter, helping to design, test, and optimize circuits without manual calculations. A low pass filter (LPF) is a circuit that passes signals with a frequency lower than a selected cutoff frequency and attenuates signals with higher frequencies. It’s one of the most common tools in electronics: from smoothing signals in power supplies to audio crossover design. This calculator allows you to choose filter circuit: RC filter or RL filter. The RC low pass passive filter consists of a resistor and a capacitor. To calculate a particular parameter of a circuit (e.g. cutoff frequency (fc), resistance (R) value or capacitance (C) value) click on the corresponding parameter on the figure and then enter all the necessary values. The RL low pass passive filter consists of a resistor and a inductor. To calculate a particular parameter of a circuit (e.g. cutoff frequency (fc), resistance (R) value or inductance (L) value) click on the corresponding parameter on the figure and then enter all the necessary values. Practical Examples1. Student Project: Signal Filtering in LabIn a basic electronics lab, students often need to analyze how a simple RC filter affects signals of different frequencies. With this setup, signals below ~1.6 kHz pass almost unchanged, while higher frequencies are attenuated. This helps students visualize frequency response, understand the concept of cutoff frequency, and prepare for more complex filter designs in advanced courses. R = 1 kΩ, C = 0.1 µF fc = 1 / 2×π×1000×1.0×10–7 ≈ 1592 Hz 2. Professional Use: Audio CrossoverAudio engineers use low-pass filters to direct bass frequencies to subwoofers while blocking mids and highs. For example, in a speaker crossover network, this RC filter ensures only frequencies below ~154 Hz reach the bass driver. Using the calculator helps professionals quickly test different resistor and capacitor values during design, saving time and ensuring high-quality sound reproduction without distortion. R = 2.2 kΩ, C = 0.47 µF fc = 1 / 2×π×2200×4.7×10–7 ≈ 154 Hz 3. Home / DIY: Power Supply Ripple FilteringIn household electronics or DIY projects, one common problem is residual AC ripple in a DC power supply. By choosing a large capacitor and small resistor, this low-pass filter attenuates unwanted ripple (usually at 50/60 Hz) while letting the DC voltage through. The calculator helps DIY hobbyists select optimal capacitor sizes, avoiding hum in audio devices, flicker in LED lights, or instability in small microcontroller projects. R = 10 Ω, C = 1000 µF fc = 1 / 2×π×10×1000×10–6 ≈ 15.9 Hz Please visit our website for free and simple use of Multifunctional engineering calculations of electronic circuits and components. |
|
Site mapPrivacy policyTerms of Use & Store PoliciesHow to BuyShippingPayment |



