| www.tmatlantic.com
Test & Soldering Equipment On-line Store |
|
D.E.V.I.C.E. (Wiki)Calculators Services |
|||||
Filter by first letter
|
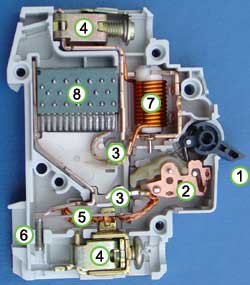
Circuit breakerA device that opens an electric circuit when the current in the circuit exceeds a certain value. Circuit breakers protect devices in electric circuits and prevent fires. All circuit breakers have common features in their operation, although details vary substantially depending on the voltage class, current rating and type of the circuit breaker. The circuit breaker must detect a fault condition; in low-voltage circuit breakers this is usually done within the breaker enclosure. Circuit breakers for large currents or high voltages are usually arranged with pilot devices to sense a fault current and to operate the trip opening mechanism. The trip solenoid that releases the latch is usually energized by a separate battery, although some high-voltage circuit breakers are self-contained with current transformers, protection relays, and an internal control power source. Once a fault is detected, contacts within the circuit breaker must open to interrupt the circuit; some mechanically-stored energy (using something such as springs or compressed air) contained within the breaker is used to separate the contacts, although some of the energy required may be obtained from the fault current itself. Small circuit breakers may be manually operated; larger units have solenoids to trip the mechanism, and electric motors to restore energy to the springs. Inside of a circuit breaker:
Sources: National Science Teachers Association (NSTApress) |
Site mapPrivacy policyTerms of Use & Store PoliciesHow to BuyShippingPayment




|